Seasonal or Cyclical Variation and Dummy Variable Technique
- Oct 25, 2014
- 2 min read
Time-Series is a time-ordered sequence of observations on a variable. Time-Series Model uses time-series history of the variable of interest to predict future values. It describes the process by which these historical data were generated.
In Time-Series Analysis, it is necessary to specify a mathematical model that represents the generating process. Here is where the regression model or the linear equation as with the empirical demand specification or function is useful again.
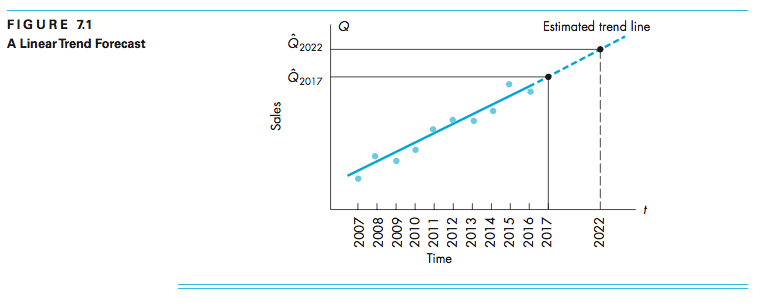
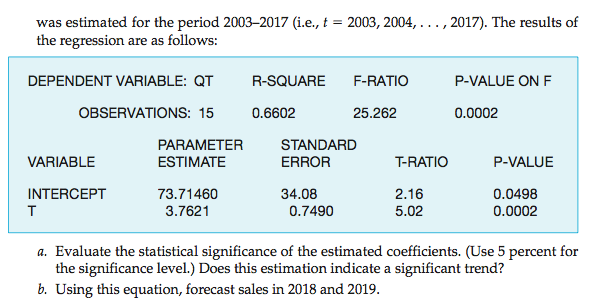
Linear Trend Forecasting
Linear trend is the simplest time-series forecasting method. Using this, one could posit that sales or price increases or decreases linearly over time.
REMINDER: It is important to test whether there is a statistically significant positive or negative trend. Use the p-value or t-test/ratio.

Let's work on a technical problem (Board Work. Solution will be in a later self-titled post.)
WHAT IF there are seasonal or cyclical variations in sales or demand, say from quarter to quarter or on a monthly basis?
Like for examples, in the retail clothing business, wherein sales tend to be generally higher before Easter and Christmas, or in the Philippine Bureau of Fire Protection, whose fire suppression services are most in demand during summer and Christmas holidays.

In Figure 7.4 (above), we can see the graphical representation of the equation below for time-series with seasonal or cyclical variations.

Seasonal or cyclical variation is a REGULAR variation that time-series data FREQUENTLY exhibit.
Failure to take such regular (and even systematic) variations into account when estimating a forecasting equation WOULD BIAS THE FORECAST.
To correct this, we use the Dummy Variable Technique. Dummy variables in time-series demand analysis account for cyclical or seasonal variation in sales. See the basic equation for this technique below.

A dummy variable is a variable that can take on only the values of "0" (for no seasonal or cyclical variation) or "1" (presence of seasonal or cyclical variation).
In a quarter time-series with - or even without - seasonal variation, below is the time-series mathematical model.


We are going to see some of those techniques in the video on the post about other demand forecasting techniques. Meanwhile, let us take note of the following points about the dummy variable technique.




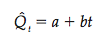
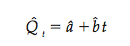
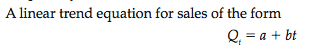





















Comments